Supraventriculaire ritmestoornissen: verschil tussen versies
Naar navigatie springen
Naar zoeken springen
Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
||
| Regel 10: | Regel 10: | ||
| [[Image:atrial_ventricular.png|300px]] | | [[Image:atrial_ventricular.png|300px]] | ||
| [[image:SVT_overview.png|300px]] | | [[image:SVT_overview.png|300px]] | ||
| [[Image:svt_algoritme.png|300px]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
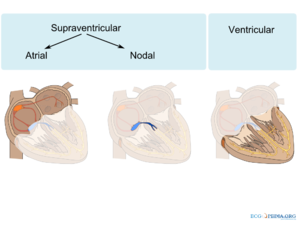
!Ritmestoornissen kunnen op verschillende manieren ingedeeld worden. Een belangrijk onderscheid is of de ritmestoornis supraventriculair (atriaal of nodaal) of ventriculair is. | !Ritmestoornissen kunnen op verschillende manieren ingedeeld worden. Een belangrijk onderscheid is of de ritmestoornis supraventriculair (atriaal of nodaal) of ventriculair is. | ||
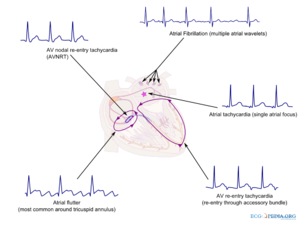
!Een overzicht van pathologische supraventriculaire tachycardiën en hun oorsprong | !Een overzicht van pathologische supraventriculaire tachycardiën en hun oorsprong | ||
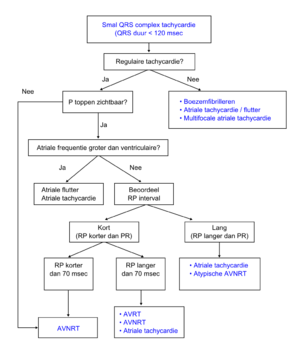
!Een algoritme om SVT's te onderscheiden<cite>ACC</cite> | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Regel 132: | Regel 134: | ||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
#ESCnarrowQRS pmid=14563598 | #ESCnarrowQRS pmid=14563598 | ||
#ACC pmid=14557344 | |||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Versie van 11 nov 2009 10:34
| Auteur | J.S.S.G. de Jong | |
| Co-Auteur | ||
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong | |
| Supervisor | ||
| Lees meer over auteurschap op ECGpedia | ||
Supraventriculaire ritmestoornissen zijn ritmestoornissen waarbij de atria deel uitmaken van de ritmestoornis. Supraventriculaire ritmestoornissen hebben over het algemeen hun oorsprong in de atria of de AV knoop. Dit in tegenstelling tot ventriculaire ritmestoornissen waar de ventrikels van het hart het ritme bepalen, onafhankelijk van de atria.
|
|
|
| Ritmestoornissen kunnen op verschillende manieren ingedeeld worden. Een belangrijk onderscheid is of de ritmestoornis supraventriculair (atriaal of nodaal) of ventriculair is. | Een overzicht van pathologische supraventriculaire tachycardiën en hun oorsprong | Een algoritme om SVT's te onderscheiden[1] |
|---|
| voorbeeld | regelmatigheid | boezemfrequentie | ventrikelfrequentie | oorsprong (SVT/VT) | p-top | effect van adenosine | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| smal complex (QRS<0.12) | |||||||
| Sinustachycardie | regulair | 100-180 bpm | 100-180 bpm | sinusknoop (SVT) | vóór het QRS complex | vertraagd geleidelijk | |
| Boezemfibrilleren | volkomen onregelmatig | 400-600 bpm | 75-175 bpm | boezems (SVT) | afwezig | vertraagd; onregelmatigheid blijft | |
| Boezemflutter | regulair (soms met wisselend blok) | 250-350 bpm | 75-150 bpm (3:1 of 2:1 blok komt het meest voor) | boezems(SVT) | negatieve zaagtand in afleiding II | tijdelijke vertraging (e.g. 4:1) | |
| AVNRT | regulair | 180-250 bpm | 180-250 bpm | AV-knoop (SVT) | in het QRS complex (R') | stopt | |
| Atriale Tachycardie | regulair | 120-250 bpm | 75-200 bpm | boezems | vóór het QRS complex, de p top heeft een andere configuratie | tijdelijk AV-blok | |
| Atrio-Ventricular Reentry Tachycardie (AVRT)- orthodroom | regulair | 150-250 bpm | 150-250 bpm | cirkel: av-knoop - ventrikels - extranodale verbinding - boezems (antrograad) | RP < PR | stopt | |
| AV junctional tachycardie | regulair | 60-100 bpm | 70-130 bpm | AV knoop | RP < PR | vertraagd | |
| Breed complex (QRS>0.12) | |||||||
| Supraventriculaire tachycardie met block | (ir)regulair afhankelijk van onderliggende SVT | 150-250 bpm | 75-200 bpm | boezems (SVT) | afwezig | vertraagd | |
| Atrio-ventricular Reentry Tachycardie (AVRT) - antidroom | regulair | 150-250 bpm | 150-250 bpm | circulair: bypass - ventricles - av-node - atria (retrograad) | RP < PR | stopt | |
Supraventriculaire ectopische slagen kunnen leiden tot
Lees ook
- Stroomdiagram: Diagnostiek van de smalcomplex tachycardie naar [2].
- Inleidend hoofdstuk ritmestoornissen
- Mechanismen van ritmestoornissen
- Sinusritme
- Nodale ritmestoornissen
- Ventriculaire ritmestoornissen
- Supraventriculaire tachycardie met aberrantie
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndroom
Referenties
- Blomström-Lundqvist C, Scheinman MM, Aliot EM, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Camm AJ, Campbell WB, Haines DE, Kuck KH, Lerman BB, Miller DD, Shaeffer CW Jr, Stevenson WG, Tomaselli GF, Antman EM, Smith SC Jr, Alpert JS, Faxon DP, Fuster V, Gibbons RJ, Gregoratos G, Hiratzka LF, Hunt SA, Jacobs AK, Russell RO Jr, Priori SG, Blanc JJ, Budaj A, Burgos EF, Cowie M, Deckers JW, Garcia MA, Klein WW, Lekakis J, Lindahl B, Mazzotta G, Morais JC, Oto A, Smiseth O, Trappe HJ, American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines, and European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines. Writing Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Supraventricular Arrhythmias. ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias--executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Supraventricular Arrhythmias). Circulation. 2003 Oct 14;108(15):1871-909. DOI:10.1161/01.CIR.0000091380.04100.84 |
- Blomström-Lundqvist C, Scheinman MM, Aliot EM, Alpert JS, Calkins H, Camm AJ, Campbell WB, Haines DE, Kuck KH, Lerman BB, Miller DD, Shaeffer CW, Stevenson WG, Tomaselli GF, Antman EM, Smith SC Jr, Alpert JS, Faxon DP, Fuster V, Gibbons RJ, Gregoratos G, Hiratzka LF, Hunt SA, Jacobs AK, Russell RO Jr, Priori SG, Blanc JJ, Budaj A, Burgos EF, Cowie M, Deckers JW, Garcia MA, Klein WW, Lekakis J, Lindahl B, Mazzotta G, Morais JC, Oto A, Smiseth O, Trappe HJ, and European Society of Cardiology Committee, NASPE-Heart Rhythm Society. ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias--executive summary. a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on practice guidelines and the European society of cardiology committee for practice guidelines (writing committee to develop guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular arrhythmias) developed in collaboration with NASPE-Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003 Oct 15;42(8):1493-531. DOI:10.1016/j.jacc.2003.08.013 |