Supraventriculaire ritmestoornissen: verschil tussen versies
Naar navigatie springen
Naar zoeken springen
Geen bewerkingssamenvatting |
|||
| (61 tussenliggende versies door 15 gebruikers niet weergegeven) | |||
| Regel 1: | Regel 1: | ||
{{auteurs| | |||
|mainauthor= [[user:Drj|J.S.S.G. de Jong]] | |||
|coauthor= | |||
|moderator= [[user:Drj|J.S.S.G. de Jong]] | |||
|supervisor= | |||
}} | |||
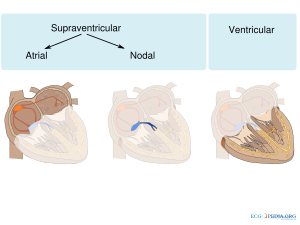
Supraventriculaire ritmestoornissen zijn ritmestoornissen waarbij de atria deel uitmaken van de ritmestoornis. Supraventriculaire ritmestoornissen hebben over het algemeen hun oorsprong in de atria of de AV-knoop. Dit in tegenstelling tot ventriculaire ritmestoornissen waar de ventrikels van het hart het ritme bepalen, onafhankelijk van de atria. | |||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" width="610px" | |||
|- | |||
| [[File:atrial_ventricular.svg|300px]] | |||
| [[image:SVT_NL.svg|300px]] | |||
| [[Image:svt_algoritme.png|300px]] | |||
|- | |||
!Ritmestoornissen kunnen op verschillende manieren ingedeeld worden. Een belangrijk onderscheid is of de ritmestoornis supraventriculair (atriaal of nodaal) of ventriculair is. | |||
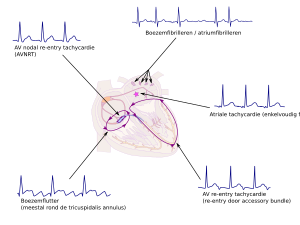
!Een overzicht van pathologische supraventriculaire tachycardieën en hun oorsprong | |||
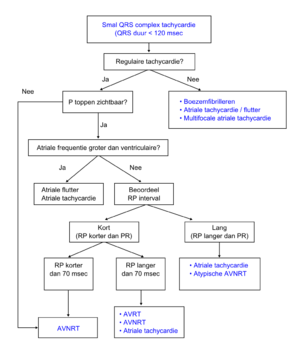
!Een algoritme om SVT's te onderscheiden<cite>ACC</cite> | |||
|} | |||
{| class="wikitable" font-size="80%" align="left" | |||
{| class="wikitable" font-size=" | |||
|- style="text-align:center;background-color:#6EB4EB;" | |- style="text-align:center;background-color:#6EB4EB;" | ||
|+''' | |+'''Overzicht van supraventriculaire tachycardieën''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
! | ! | ||
! | !voorbeeld | ||
! | !regelmatigheid | ||
! | !boezemfrequentie | ||
! | !ventrikelfrequentie | ||
! | !oorsprong (SVT/VT) | ||
!effect | !P-top | ||
![[effect van adenosine]] | |||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="8" style="text-align:left;background-color:#cfefcf;" | ''' | | colspan="8" style="text-align:left;background-color:#cfefcf;" | '''smal complex (QRS < 0,12)''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
! [[ | ! [[Sinustachycardie]] | ||
| | | [[Image:sinustachy_small.svg|200px]] | ||
| 100- | | regulair | ||
| 100- | | 100-210 bpm | ||
| | | 100-210 bpm | ||
| | | sinusknoop (SVT) | ||
| | | vóór het QRS-complex | ||
| vertraagt geleidelijk | |||
|- | |- | ||
! [[ | ! [[Boezemfibrilleren]] | ||
| | | [[Image:afib_small.svg|200px]] | ||
| volkomen onregelmatig | |||
| 400-600 bpm | | 400-600 bpm | ||
| 75-175 bpm | | 75-175 bpm | ||
| | | boezems (SVT) | ||
| | | afwezig | ||
| | | vertraagt; onregelmatigheid blijft | ||
|- | |- | ||
! [[ | ! [[Boezemflutter]] | ||
| | | [[Image:aflutt_small.svg|200px]] | ||
| regulair (soms met wisselend blok) | |||
| 250-350 bpm | | 250-350 bpm | ||
| 75-150 bpm (3:1 | | 75-150 bpm (3:1 of 2:1 blok komt het meest voor) | ||
| | | boezems(SVT) | ||
| | | negatieve zaagtand in afleiding II | ||
| | | tijdelijke vertraging (b.v. 4:1) | ||
|- | |- | ||
! [[AVNRT]] | ! [[AVNRT]] | ||
| | | [[Image:avnrt_small.svg|200px]] | ||
| | | regulair | ||
| | | 100-280 bpm, meestal rond 170 bpm | ||
| AV- | | 100-280 bpm | ||
| in QRS complex (R') | | AV-knoop (SVT) | ||
| | | in het QRS-complex (R') | ||
| stopt | |||
|- | |- | ||
! [[ | ! [[Atriale Tachycardie|Atriale tachycardie]] | ||
| | | [[Image:atrialtachy_small.svg|200px]] | ||
| regulair | |||
| 120-250 bpm | | 120-250 bpm | ||
| 75-200 bpm | | 75-200 bpm | ||
| | | boezems | ||
| | | vóór het QRS-complex, de P-top heeft een andere configuratie | ||
| | | tijdelijk AV-blok | ||
|- | |- | ||
! [[AVRT| | ! [[AVRT|Atrioventriculaire re-entrytachycardie (AVRT) - orthodroom]] | ||
| | | [[Image:avrt_small.svg|200px]] | ||
| regulair | |||
| 150-250 bpm | | 150-250 bpm | ||
| 150-250 bpm | | 150-250 bpm | ||
| | | cirkel: AV-knoop - ventrikels - extranodale verbinding - boezems (anterograad) | ||
| RP < PR | | RP < PR | ||
| | | stopt | ||
|- | |- | ||
! [[AVJT|AV | ! [[AVJT|AV-junctionale tachycardie]] | ||
| | | [[Image:avnodal_small.svg|200px]] | ||
| regulair | |||
| 60-100 bpm | | 60-100 bpm | ||
| 70-130 bpm | | 70-130 bpm | ||
| AV | | AV-knoop | ||
| RP < PR | | RP < PR | ||
| | | vertraagt | ||
|- | |- | ||
| colspan="8" style="text-align:left;background-color:#cfefcf;" | ''' | | colspan="8" style="text-align:left;background-color:#cfefcf;" | '''Breed complex (QRS > 0,12)''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
! [[ | ! [[SVT met aberrantie|Supraventriculaire tachycardie met aberrantie (LBTB of RBTB)]] | ||
| (ir) | | [[Image:atrial_tachy_with_LBBB_leadII.svg|200px]] | ||
| | | (ir)regulair afhankelijk van onderliggende SVT | ||
| | | > 100 bpm | ||
| | | > 100 bpm | ||
| | | boezems (SVT) | ||
| | | afwezig | ||
| vertraagt | |||
|- | |- | ||
! [[AVRT| | ! [[AVRT|Atrioventriculaire re-entrytachycardie (AVRT) - antidroom]] | ||
| | | | ||
| regulair | |||
| 150-250 bpm | | 150-250 bpm | ||
| 150-250 bpm | | 150-250 bpm | ||
| | | cirkel: bypass - ventrikels - AV-knoop - atria (retrograad) | ||
| RP < PR | | RP < PR | ||
| | | stopt | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
== | ===Supraventriculaire [[ectopische slagen]] kunnen leiden tot=== | ||
*[[Boezemextrasystole]] | |||
*[[Wandering pacemaker]] | |||
===Lees ook=== | |||
*[[Ritmestoornissen|Inleidend hoofdstuk ritmestoornissen]] | |||
*[[Mechanismen van ritmestoornissen]] | |||
*[[Sinusritme]] | |||
*[[Nodale ritmestoornissen]] | |||
*[[Ventriculaire ritmestoornissen]] | |||
*[[SVT met aberrantie|Supraventriculaire tachycardie met aberrantie]] | |||
*[[WPW|Wolff-Parkinson-White-syndroom]] | |||
==Referenties== | |||
<biblio> | <biblio> | ||
# | #ACC pmid=14557344 | ||
</biblio> | </biblio> | ||
Huidige versie van 3 feb 2021 22:40
| Auteur | J.S.S.G. de Jong | |
| Co-Auteur | ||
| Moderator | J.S.S.G. de Jong | |
| Supervisor | ||
| Lees meer over auteurschap op ECGpedia | ||
Supraventriculaire ritmestoornissen zijn ritmestoornissen waarbij de atria deel uitmaken van de ritmestoornis. Supraventriculaire ritmestoornissen hebben over het algemeen hun oorsprong in de atria of de AV-knoop. Dit in tegenstelling tot ventriculaire ritmestoornissen waar de ventrikels van het hart het ritme bepalen, onafhankelijk van de atria.
| voorbeeld | regelmatigheid | boezemfrequentie | ventrikelfrequentie | oorsprong (SVT/VT) | P-top | effect van adenosine | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| smal complex (QRS < 0,12) | |||||||
| Sinustachycardie | regulair | 100-210 bpm | 100-210 bpm | sinusknoop (SVT) | vóór het QRS-complex | vertraagt geleidelijk | |
| Boezemfibrilleren | volkomen onregelmatig | 400-600 bpm | 75-175 bpm | boezems (SVT) | afwezig | vertraagt; onregelmatigheid blijft | |
| Boezemflutter | regulair (soms met wisselend blok) | 250-350 bpm | 75-150 bpm (3:1 of 2:1 blok komt het meest voor) | boezems(SVT) | negatieve zaagtand in afleiding II | tijdelijke vertraging (b.v. 4:1) | |
| AVNRT | regulair | 100-280 bpm, meestal rond 170 bpm | 100-280 bpm | AV-knoop (SVT) | in het QRS-complex (R') | stopt | |
| Atriale tachycardie | regulair | 120-250 bpm | 75-200 bpm | boezems | vóór het QRS-complex, de P-top heeft een andere configuratie | tijdelijk AV-blok | |
| Atrioventriculaire re-entrytachycardie (AVRT) - orthodroom | regulair | 150-250 bpm | 150-250 bpm | cirkel: AV-knoop - ventrikels - extranodale verbinding - boezems (anterograad) | RP < PR | stopt | |
| AV-junctionale tachycardie | regulair | 60-100 bpm | 70-130 bpm | AV-knoop | RP < PR | vertraagt | |
| Breed complex (QRS > 0,12) | |||||||
| Supraventriculaire tachycardie met aberrantie (LBTB of RBTB) | (ir)regulair afhankelijk van onderliggende SVT | > 100 bpm | > 100 bpm | boezems (SVT) | afwezig | vertraagt | |
| Atrioventriculaire re-entrytachycardie (AVRT) - antidroom | regulair | 150-250 bpm | 150-250 bpm | cirkel: bypass - ventrikels - AV-knoop - atria (retrograad) | RP < PR | stopt | |
Supraventriculaire ectopische slagen kunnen leiden tot
Lees ook
- Inleidend hoofdstuk ritmestoornissen
- Mechanismen van ritmestoornissen
- Sinusritme
- Nodale ritmestoornissen
- Ventriculaire ritmestoornissen
- Supraventriculaire tachycardie met aberrantie
- Wolff-Parkinson-White-syndroom
Referenties
<biblio>
- ACC pmid=14557344
</biblio>